ASCII.jp Understand the DDOS "Syn flood attack" that uses a false IP address
A series of DDOS attacks by the United States security vendor "Arbor Networks", which develops and sells the DDOS detection solution "PeakflowSP".The first one has seen the DDOS attack, and the second is the DDOS attack method.Next, let's look at the types of DDOS attacks that are important in understanding DDOS attacks.
DDOS attack from a false IP address
If the type of DDOS attack is roughly divided into two, it can be distinguished from "attacks from false IP addresses (spood IP)" and "attacks from the actual existing IP address".This time, I will introduce the former attack from the former false IP address.
The method of DDOS attacks is roughly divided into two
Unfortunately, in the current IP implementation, the packet can be delivered to the other party even if you fake your own IP address (source IP address) unless a special setting is made in the router that relays packets.is.This is said to be similar to the delivery of letters.Even if you write your address falsely, if the destination is correct, it will reach the other party.The same is true for the IP world.The reason for disguising the source IP address is simple, because the attacker is not identified.
The famous attack, "Syn Flood Attack (TCP Syn FLOOD)", uses its mechanism.To understand this, first remember the basics of TCP, the so -called 3 -way hand shake.To the first Syn packet sent from the client, the server receives Syn/ACK.The client, on the other hand, is established by reply to ACK to the server.In this series of actions, the server is waiting for the ACK from the client when the Syn/ACK responds.
What is SYN flood attack?
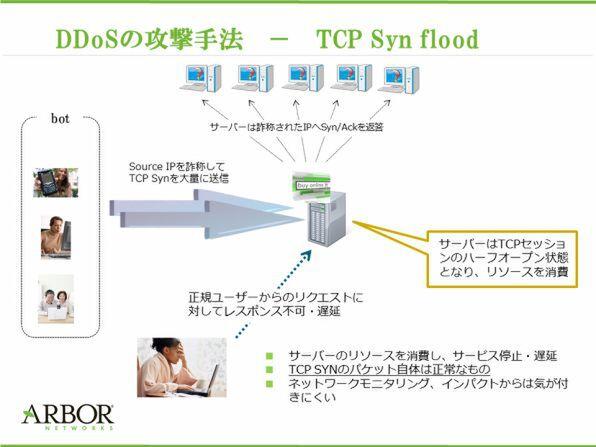
Then, what would happen if the client sends the client's own IP address as a source IP address at the stage of sending the Syn packet for the first time?The server naturally responds to the IP address that falsifies Syn/ACK.This false IP address may exist or not somewhere in the world.Even if it exists, devices with the IP address do not respond to Syn/ACK sent from a stranger server.Therefore, the server will continue to wait for ACK from a false IP address.
Sending packets using a false IP address can be easily realized by using simple tools.If such a packet came from the bot introduced last time, the number would be hundreds of thousands to millions, and the server resources would be easily depleted.This is the horror of the Syn flood.
As an aside, if all bot sends Syn with a false IP address, the device with this IP address looks like an attacker receiving Syn/ACK.Servers and clients do not process the sudden Syn/ACK packets, so they are not directly affected, but depending on the amount, the network can be congested.Interestingly, looking at the source address of Syn/ACK, you can identify who is currently attacking.This is one of the DDOS observations.
Matt Moinahan, a Senior Vice President of the United States, who came to Japan at the end of 2012.With the cooperation of telecommunications businesses around the world that adopts the company's products, it is always monitoring about 30 % of all traffic on the Internet, which is useful for DDOS attacks.
"UDP Flood" is an attack from a false IP address, but a simpler attack.Since UDP is a connectivity communication, packets can be sent unilaterally.In addition, UDP can send up to 1500 byte packets as normal communication.For example, only 65,000 bots sent a 1500 -byte packet per second, which reaches about 100 Mbps.
If you send 10 packets, it will be 1Gbps.The recent PC ability has improved dramatically, and the amount of packet transmissions when manipulated as a bot is enormous.UDP flood is unlikely to affect the server resources directly, but the communication amount of the network connected to the server is depleted, resulting in no communication to the server.
There is also a "Fragment Attack" attack from a false IP address.Fragment is an IP fragment.Packets with a long data length are divided and sent to the destination, but the server that receives it needs to return the split packet to the original data, accumulating packets on the memory.Fragment attacks are intended to exhaust server resources by continuously sending split packets to the server.
Regarding the three attacks introduced this time, each one cannot be distinguished from normal IP communication if viewed in packets.This is one of the difficult reasons for DDOS defense, that is, the weakness of IP.However, the Internet is an IP network, and it is clear that this weakness should be applied immediately.
Next time, let's introduce the complicated DDOS attack.
Arber Networks Co., Ltd. Nippon Office SE Manager.Since 2000, he has been in charge of NTT East and TEPCO as PRE-SALES SE at Cisco Systems.In 2004, he transferred to Erakoya Networks and proposed a solution for application identification using DPI technology.Incumbent since 2008




![[July 6 and 7] DX realized by content cloud, advanced platform for business transformation](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/6bbafe438d78271513761788166cbf94_0.jpeg)

