Network Location AWARENESS and Network Profile to identify the network status on Windows
NLA that provides information on whether the current machine is connected to the network or Internet or local
Network Location AWARENESS (NLA) is a function that identifies the connected network for applications that access the server in the LAN and provide information on which network connected.
In the first place, before the cloud services become common as today (until the first half of 2000), it is common for local servers (so -called on -premises servers) to provide various services in companies.is.At this time, the application that accesses such a local server needs to distinguish the connected network and perform appropriate actions.
The network connected by the desktop PC rarely changes, but a PC that can be carried around, such as a notebook PC, may be cut from a network or a completely different network.。In addition, not only wired, but also multiple interfaces such as wireless LAN, modem communication, and VPN may be used properly.
At this time, it took time for the application to find out that the application would not be accessible, for example, if it was not connected to the network.It is not possible to know in advance whether or not to communicate with the other party, and "not being able to communicate" can only be determined because there is no response from the other party.To do so, you need to wait to confirm that there is no response for a certain period of time.And in some cases, the load on the server may be heavy and the response may be delayed.
Also, even if you connect to the network, it may not be accessible to the expected server because it is another network.Alternatively, the services that are running on the server may not have the right to access the server.
For this reason, the application that uses the network needs to identify the connected network status and the connected network.Since the server on the Internet side is used, simply using the domain name and obtaining an IP address, you can always access unless your opponent stops.From the client's point of view, it is easier to access the cloud than to access on -premises (local servers).
In Windows 10, switch firewalls and printer shared functions depending on the location of the network.
So, in order for the app to determine the network, Windows had a simple network identification function in XP.In XP, the active directory was able to distinguish between the "domain network" and the non -domain network.In SP2, a firewall was introduced, and at this time, the connected network could switch the rules of the firewall.Windows Vista was the NLA proceeding.
In NLA, it can distinguish whether it is connected to the network (whether there is a network), whether it is a domain network, a single network, or a state of connecting to multiple networks.Then, based on the discrimination results, the application can notify the application of withdrawal, connection from the network, and which network has been connected.
Windows itself also uses this function so that Windows 10 can be switched by a network that connects "Firewall rules" and "File and Printer Sharing".The so -called "network location" (private network, public network, domain network) uses NLA functions.
NLA creates a profile and identifies the same network.
Specifically, NLA creates a "profile" of the connected network (hereinafter referred to as a network profile), and then identifies whether it is the same network.This network profile consists of information such as the location of the network and the type of network.However, the network profile itself does not include network information such as IP addresses.
For example, if you connect to both wireless LAN and Ethernet on your home laptop, you may have seen the connection network displayed as a wireless LAN SSID when connected by Ethernet.This is not a bug, but the NLA network identification features indicate that Windows has determined that they are "the same network" apart from physical connection methods.
By the way, by editing the network profile registered in the registry, you can rewrite the name of the network displayed by Windows.
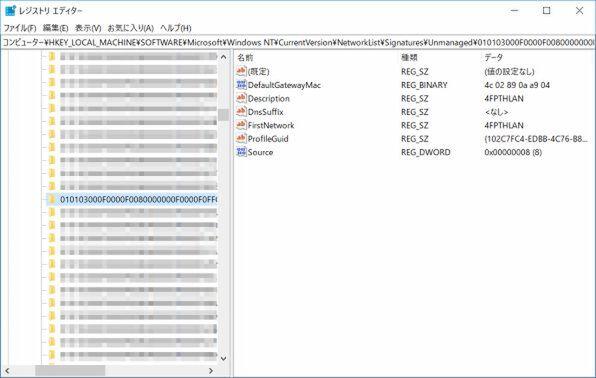
This network profile is stored in the registry.Location,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows NT \ CurrentVersion \ Networklist \ Profiles
It is in.Here, the GUID format key is registered, each of which is a network profile.
The profile is the key name of the GUID, and the first connection date and time and the last connection are also recorded.
The stored information is shown in the table below.The most important here is Category, NameType, and Profilename.
Category is information corresponding to the location of the network.The value of this DWORD value (32bit integer) is a public = 0, private (home) = 1, domain (work) = 2.The initial value is "public", but if it is connected to a domain network, it can be automatically designated and becomes a "domain".In addition, the user can specify "private" for "public" network (it will not be private unless the user specifies).
NameType represents the type of connection.For example, 63 for Ethernet, 71 for wireless LAN, and 243 for mobile broadband (mobile phone network).
This is a value defined by Microsoft and included in Windows SDK..The file "H" contains the definition.
Since it simply supports the network and integer value, the value itself is meaningless.However, looking at this value, you can distinguish whether it is a profile created when connected by the network and Ethernet or a profile created when connected by wireless LAN.In addition, the profile records the first connection date and time (the date and time when the profile was created) and the last connected date and time.
ProfileName is a name that distinguishes the connected network.Profilename is displayed in the "connection" of the control panel network and the shared center, "Setting App" → "Network and Internet" → "Change Connection Properties", and rewrite this value in the registry.And the display can be changed.
Information for distinguishing this network profile is called a signature.If it is a non -domain network, the MAC address of the gateway (router) in the network will be registered.With the same network, it should be connected to the same router, and for wireless LAN or Ethernet, the router should be the same device for the same network.
The MAC address is a physical hardware address of Ethernet and wireless LAN, with a unique value assigned for each hardware, and there is no network device with the same value.Therefore, if the MAC address is the same, it can be judged as the same physical router.
This signature is
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows NT \ CurrentVersion \ Networklist \ SignatureS
It is registered below.
The signature contains information to identify the network, and has a MAC address and DNS sapix of the default gateway (router).There is a professional GUID corresponding to this
This signature has a key name (GUID format) registered with the MAC address of the router and the above -mentioned network profile.
NLA finds the signature of the connection destination network from the MAC address of the router, and identifies the network profile from the registered ProfileGuid.This network signature also has a DNS safics.The DNS sapix is the second half of the domain name that is supplemented by default when only the host name is specified when specifying the DNS name.
If the name is resolved by DNS, if the other party is specified only with the host name in the local environment, if this is the formal domain name (FQND, Fully Qualified Domain Name), the host name.The part that is applied after is called "DNS Safix".In general, the DHCP server specifies this.The fact that the network has the same DNS safics means that you belong to the same domain network.
However, in the actual network, a physical connection to a physical network is essential.Windows also manages information about the "interface" hardware used for network connections.However, since network hardware has developed over time, interfaces such as Ethernet, wireless LAN, and mobile broadband are managed separately.
For example, wireless LAN was taken into Windows later than Ethernet.For this reason, wireless LAN management and Ethernet management are different.Next time, let's look at this "profile".




![[July 6 and 7] DX realized by content cloud, advanced platform for business transformation](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/6bbafe438d78271513761788166cbf94_0.jpeg)

